CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Course
-
About the course and exam
About the course and certification -
About the course author
-
Pre-requisites
-
Tools and tips to help you study more efficiently
-
Study techniques that will help you pass
-
What surprised me the most about the exam
-
Domain 1: Threats, Attacks, and VulnerabilitiesAbout threats, attacks, and vulnerabilities
-
1.1: Compare and contrast social engineering techniquesWhat is social engineering?
-
Principles
-
Spam
-
Blocking and Managing Spam
-
Phishing
-
Smishing
-
Vishing
-
Spear Phishing
-
Whaling
-
Impersonation
-
Dumpster diving
-
Shoulder surfing
-
Pharming
-
Tailgating
-
Eliciting information
-
Prepending
-
Identity fraud
-
Invoice scams
-
Credentials harvesting
-
Reconnaissance
-
Hoax
-
Watering hole attack
-
Typo squatting and URL hijacking
-
Influence campaigns
-
Hybrid warfare
-
Practical knowledge check
-
1.2: Analyze potential indicators to determine the type of attackWhat is malware?
-
Malware classification
-
Virus
-
Worms
-
Backdoor
-
Trojans
-
Remote Access Trojan (RAT)
-
Ransomware and Crypto Malware
-
How does ransomware work?
-
Potentially unwanted programs (PUPs)
-
Spyware
-
Adware and Malvertising
-
Keyloggers
-
Fileless malware
-
Logic bombs
-
Rootkit
-
Bots and Botnets
-
Command and control
-
What are password attacks?
-
Plaintext, encrypted, and hashed passwords
-
Brute force
-
Dictionary attacks
-
Spraying attacks
-
Rainbow and hash tables
-
Credential stuffing
-
What are physical attacks?
-
Malicious universal serial bus (USB) cable
-
Malicious flash drive
-
Card cloning
-
Skimming
-
What is adversarial AI and tainted training for ML?
-
Supply-chain attacks
-
Cloud-based vs. on-premises attacks
-
Cryptography concepts
-
Cryptographic attacks
-
Quiz: 1.23 Quizzes
-
1.3: Analyze potential indicators associated with application attacksPrivilege escalation
-
Improper input handling
-
Improper error handling
-
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
-
Structured Query Language (SQL) injections
-
Dynamic Link Library (DLL) Injections
-
Lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) Injections
-
Extensible Markup Language (XML) and XPATH Injections
-
XXE Injections
-
Directory traversal
-
Request forgeries (server-side, client-side, and cross-site)
-
Application Programming Interface (API) attacks
-
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) stripping
-
Replay attacks (session replays)
-
Pass the hash
-
Race conditions (time of check and time of use)
-
Resource exhaustion
-
Memory leak
-
Pointer/object dereference
-
Integer overflow
-
Buffer overflows
-
Driver manipulation (shimming and refactoring)
-
Quiz 1.32 Quizzes
-
1.4: Analyze potential indicators of network attacksWhat are wireless attacks?
-
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
-
Rogue access point and Evil Twin
-
Bluesnarfing and Bluejacking
-
Disassociation and Jamming
-
Radio Frequency Identifier (RFID) attacks
-
Near Field Communication (NFC)
-
Initialization Vector (IV)
-
Man in the middle (on-path)
-
Man in the browser (on-path browser)
-
What are layer 2 attacks?
-
Address resolution protocol (ARP)
-
Media access control (MAC) flooding
-
MAC cloning
-
What are Domain Name System (DNS) attacks and defenses?
-
Domain hijacking
-
DNS poisoning
-
Universal resource locator (URL) redirection
-
Domain reputation
-
Quiz 1.41 Quiz
-
1.5: Explain threat actors, vectors, and intelligence sourcesWhat are actors and threats?
-
Attributes of actors
-
Vectors
-
Insider threats
-
State actors
-
Hacktivists
-
Script kiddies
-
Hackers (white hat, black hat, gray hat)
-
Criminal syndicates
-
Advanced persistent threats (APTs)
-
Shadow IT
-
Competitors
-
Threat intelligence sources (OSINT and others)
-
Using threat intelligence
-
Research sources
-
Quiz 1.51 Quiz
-
1.6: Security concerns associated with various vulnerabilitiesCloud-based vs. on-premises vulnerabilities
-
Zero-day vulnerabilities
-
Weak configurations
-
Weak encryption, hashing, and digital signatures
-
Third-party risks
-
Improper or weak patch management
-
Legacy platforms
-
Impacts
-
Quiz 1.61 Quiz
-
1.7: Summarizing techniques used in security assessmentsThreat hunting
-
Vulnerability scans
-
Security information and event management (SIEM) and Syslog
-
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR)
-
Quiz 1.71 Quiz
-
1.8: Explaining techniques used in penetration testingImportant pentesting concepts
-
Bug bounties
-
Exercise types (red, blue, white, and purple teams)
-
Passive and active reconnaissance
-
Quiz 1.81 Quiz
-
Domain 2: Architecture and DesignAbout architecture and design
-
2.1: Explaining the importance of security concepts in an enterprise environmentConfiguration management
-
Data sovereignty
-
Data protection
-
Hardware security module (HSM) and Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
-
Geographical considerations
-
Cloud access security broker (CASB)
-
Response and recovery controls
-
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) inspection
-
Hashing
-
API considerations
-
Site resiliency
-
Deception and disruption
-
Quiz 2.11 Quiz
-
2.2: Virtualization and cloud computing conceptsComparing cloud models
-
Cloud service providers
-
Virtualization
-
Containers
-
Microservices and APIs
-
Serverless architecture
-
MSPs and MSSPs
-
On-premises vs. off-premises
-
Edge computing
-
Fog computing
-
Thin client
-
Infrastructure as Code
-
Services integration
-
Resource policies
-
Transit gateway
-
Quiz 2.21 Quiz
-
2.3: Secure application development, deployment, and automation conceptsUnderstanding development environments
-
Automation and scripting
-
Version control
-
Secure coding techniques
-
Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)
-
Integrity measurement
-
Software diversity
-
Provisioning and deprovisioning
-
Elasticity
-
Scalability
-
Quiz 2.31 Quiz
-
2.4: Authentication and authorization design conceptsImportant authentication and authorization concepts
-
Multifactor authentication (MFA) factors and attributes
-
Quiz: MFA factors and attributes1 Quiz
-
Authentication technologies
-
Biometrics techniques and concepts
-
Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA)
-
Cloud vs. on-premises requirements
-
Quiz 2.41 Quiz
-
2.5: Implementing cybersecurity resilienceWhat is redundancy?
-
Disk redundancy (RAID levels)
-
Network redundancy
-
Power redundancy
-
Replication
-
Backup types (full, incremental, differential, and snapshot)
-
Backup types practice scenarios
-
Backup devices and strategies
-
Quiz: Backup types, devices, and strategies1 Quiz
-
Non-persistence
-
Restoration order
-
Diversity
-
Quiz 2.51 Quiz
-
2.6: Security implications of embedded and specialized systemsWhat are embedded systems?
-
System on a Chip (SoC)
-
SCADA and ICS
-
Internet of Things (IoT)
-
Specialized systems
-
VoIP, HVAC, Drones/AVs, MFP, RTOS, Surveillance systems
-
Communication considerations
-
Important constraints
-
2.7: Importance of physical security controlsBollards/barricades, Mantraps, Badges, Alarms, Signage
-
Lighting and fencing
-
Cameras and Closed-circuit television (CCTV)
-
Industrial camouflage
-
Personnel, robots, drones/UAVs
-
Locks
-
Different sensors
-
Fire suppression
-
Protected cable distribution (PCD)
-
Secure areas (air gap, faraday cages, DMZ, etc…)
-
Hot and cold aisles
-
Secure data destruction
-
USB data blocker
-
Quiz 2.71 Quiz
-
2.8: Basics of cryptographyCommon use cases
-
Key length
-
Key stretching
-
Salting, hashing, digital signatures
-
Perfect forward secrecy
-
Elliptic curve cryptography
-
Ephemeral
-
Symmetric vs. asymmetric encryption
-
Key exchange
-
Cipher suites
-
Modes of operation
-
Lightweight cryptography and Homomorphic encryption
-
Steganography
-
Blockchain
-
Quantum and post-quantum
-
Limitations
-
Quizzes 2.82 Quizzes
-
Domain 3: ImplementationAbout implementation
-
3.1: Implement Secure ProtocolsImportant protocols to know and use cases
-
Important email secure protocols
-
IPsec and VPN
-
FTPS, SFTP, SCP
-
DNSSEC
-
SRTP and NTPsec
-
DHCP
-
SNMP and SNMPv3
-
Quiz 3.11 Quiz
-
3.2: Implement host or application security solutionsEndpoint protection
-
Self-encrypting drive (SED), full disk encryption (FDE), and file-level encryption
-
Boot integrity
-
Database and data security
-
Application security
-
Hardening hosts
-
Sandboxing
-
Quiz 3.21 Quiz
-
3.3: Implement secure network designsDNS
-
Load balancing
-
Network segmentation
-
East-West and North-South
-
Jump servers (bastion hosts)
-
Network Address Translation (NAT) Gateway
-
Proxy servers
-
Out-of-band management
-
Quiz 3.3.11 Quiz
-
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and IPsec
-
Network Access Control (NAC)
-
Port security
-
Network-based intrusion detection system (NIDS) and network-based intrusion prevention system (NIPS)
-
Firewalls
-
Next-Generation Firewalls
-
Access Control List (ACL) and Security Groups (SGs)
-
Quiz 3.3.21 Quiz
-
Quality of Service (QoS)
-
Implications of IPv6
-
Port scanning and port mirroring
-
File integrity monitors
-
Quiz 3.3.31 Quiz
-
3.4: Install and configure wireless security settingsCryptographic protocols
-
Methods
-
Authentication protocols
-
Installation considerations
-
Quiz 3.41 Quiz
-
3.5: Implement secure mobile solutionsConnection methods and receivers
-
Mobile deployment models
-
Mobile device management (MDM)
-
Mobile devices
-
Enforcement and monitoring
-
Quiz 3.51 Quiz
-
3.6: Apply cybersecurity solutions to the cloudCloud security controls
-
Secure cloud storage
-
Secure cloud networking
-
Secure cloud compute resources
-
Secure cloud solutions
-
Quiz 3.61 Quiz
-
3.7: Implement identity and account management controlsUnderstanding identity
-
Account types to consider
-
Account policies to consider
-
Quiz 3.71 Quiz
-
3.8: Implement authentication and authorization solutionsAuthentication management
-
Authentication protocols and considerations
-
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
-
RADIUS and TACACS+
-
Kerberos, LDAP, and NTLM
-
Federated Identities
-
Access control schemes
-
Recap notes from this section
-
Quiz 3.81 Quiz
-
3.9: Implement public key infrastructureWhat is public key infrastructure?
-
Types of certificates
-
Certificate formats
-
Important concepts
-
Quiz 3.91 Quiz
-
4.0: Operations and Incident ResponseAbout operations and incident response
-
4.1: Use the appropriate tools to assess organizational securityNetwork reconnaissance and discovery part 1
-
Network reconnaissance and discovery part 2
-
File manipulation
-
Shell and script environments
-
Packet capture and replay
-
Forensics tools
-
Exploitation frameworks
-
Password crackers
-
Data sanitization
-
Quiz 4.11 Quiz
-
4.2: Policies, processes, and procedures for incident responseIncident response plans
-
Incident response process
-
Important exercises
-
Important attack frameworks
-
BCP, COOP, and DRP
-
Incident response team and stakeholder management
-
Retention policies
-
Quiz 4.21 Quiz
-
4.3: Using appropriate data sources to support investigations after an incidentVulnerability scan outputs
-
SIEM dashboards
-
Log files
-
Syslog, rsyslog, syslog-ng
-
Journald and journalctl
-
NXLog
-
Bandwidth and network monitors
-
Important and useful metadata
-
Quiz 4.31 Quiz
-
4.4: Applying mitigation techniques or controls to secure environments during an incidentReconfiguring endpoint security solutions
-
Configuration changes
-
Isolation, containment, and segmentation
-
Secure Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
-
Quiz 4.41 Quiz
-
4.5: Key aspects of digital forensicsDocumentation and evidence
-
E-discovery, data recovery, and non-repudiation
-
Integrity and preservation of information
-
Acquisition
-
On-premises vs. cloud
-
Strategic intelligence and counterintelligence
-
Quiz 4.51 Quiz
-
Domain 5: Governance, Risk, and ComplianceAbout governance, risk and compliance
-
5.1: Compare and contrast various types of controlsCategories
-
Control types
-
Quiz 5.11 Quiz
-
5.2: Applicable regulations, standards, or frameworks that impact organizational security postureRegulations, standards, and legislation
-
Key frameworks to know about
-
Benchmarks and secure configuration guides
-
Quiz 5.21 Quiz
-
5.3: Importance of policies to organizational securityPersonnel
-
User training
-
Third-party risk management
-
Data
-
Credential policies
-
Organizational policies
-
Quiz 5.31 Quiz
-
5.4 Risk management processes and conceptsTypes of risks
-
Risk management strategies
-
Risk analysis
-
Disasters
-
Business impact analysis
-
Quiz 5.41 Quiz
-
5.5: Privacy and sensitive data concepts in relation to securityOrganizational consequences of privacy breaches
-
Notifications of breaches
-
Data types
-
Privacy enhancing technologies
-
Roles and responsibilities
-
Quiz 5.51 Quiz
-
Course Recap and Next StepsLooking for the practice exams?
-
Receiving your Certificate of Completion
It’s very easy to confuse viruses with worms, and again, the two terms are oftentimes interchanged.
In fact, if we look at this article from HP, we can see that the article is titled “The Top 10 Worst Computer Viruses in History,” yet the vast majority of these start by saying “…this is actually a worm.”
The reason for this is because viruses and worms have a subtle difference, and that difference is important to understand.
Viruses require both some sort of human or program interaction to execute, and they require a software host to spread to. Worms, on the other hand, do not.
They are designed to self-replicate via vulnerabilities in operating systems, and they spread to others throughout networks. They are usually self-contained programs that enter devices via normal communication channels and then run their own commands.
In fact, because of how good worms are at spreading to other devices, they’re often used by malicious actors to deliver other payloads.

Let me illustrate with some examples.
The Morris Worm
One of the first computer worms to ever be distributed via the Internet is known as the Morris Worm.
The Morris Worm was unleashed on November 2nd, 1988, from a computer at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Within 24 hours, roughly 6,000 out of 60,000 computers connected to the Internet on campus were infected with this worm. The program then spread to other networks, including NASA, Harvard, Princeton, Stanford, and others. This was before the World Wide Web existed, or it probably would have been much worse.

This worm wasn’t necessarily designed to do anything malicious, but it caused systems to grind to a halt and go down, which rendered those systems useless for a certain period of time.
If you’d to learn more about this interesting story, check out this article.
Mydoom
Going back to the HP article, let’s take a look at some of the most damaging worms in history.
- Mydoom – $38 bn damages in 2004
- Sobig – $30 bn damages in 2003
- Klez – $19.8bn damages in 2001
- ILOVEYOU – $15bn damages in 2000
The top mentioned worm in terms of financial damage caused is called Mydoom. This worm was spread by mass emailing, and apparently, Mydoom was responsible for 25% of all emails sent at one point.
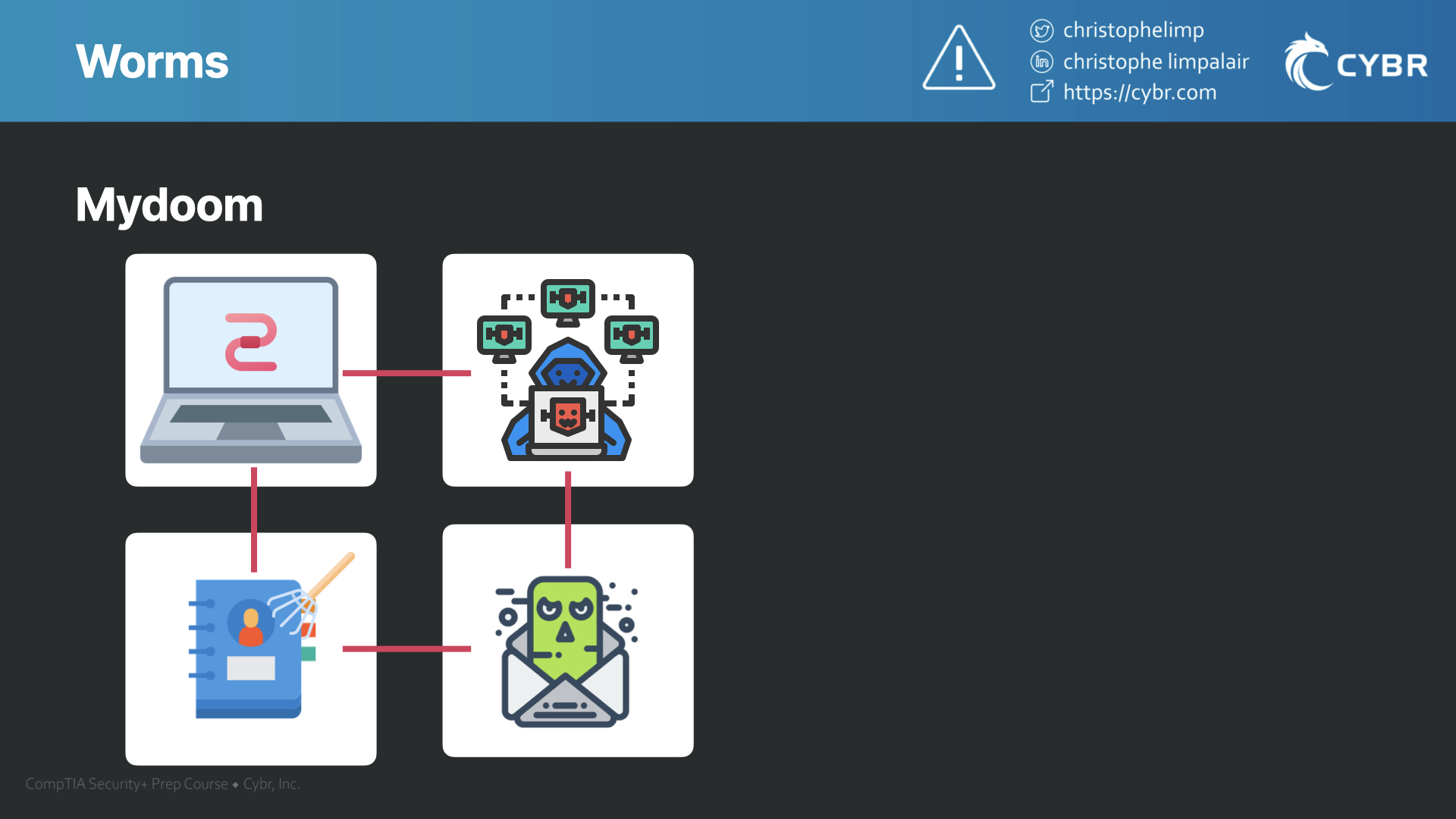
It would scrape email addresses from infected machines, then send copies of itself to all of those addresses. At the same time, it would also turn those devices into bots creating what’s called a botnet, and which we’ll talk about in another lesson.
One thing that many of these worms have in common, is that they’re spread via email. Attackers have realized that this can be a highly effective way of spreading malicious software, which is why many of the most damaging types were designed to spread this way.
Conclusion
As we wrap up this lesson, remember that the key similarities and differences between worms and viruses are:
- Viruses require some sort of activation, worms do not
- Both worms and viruses are designed to self-replicate
- Viruses latch on to other software
- Worms spread through vulnerabilities
With that, let’s mark this lesson as complete and move on to the next!


Responses